Monday, January 30, 2012
SoulMateIcon
SoulMateIcon says: "The information stored inside the SMI about ones character, age, temperament and education is based on a small questionnaire. The methodology behind this is new and it is based on the work of Gaston Berger, Joseph M. Helms, Jean Emile Charon and others. Tests have shown remarkable results: a group of 267 couples showed a 76% result of ' very accurate profiler '. "
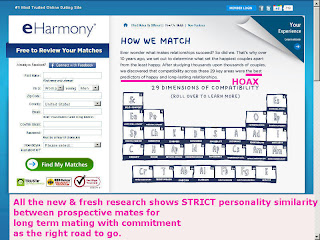
That SMI is only a HOAX based solely on a modified IPSATIVE personality test, like PerfectMatch.
Please remember.
Personality is composed of two basic types of traits:
traits that an individual acquires, dimensions of character;
and
traits with biological underpinnings, dimensions of temperament (Cloninger 1987).
IPSATIVE personality tests are OBSOLETE (self-descriptive questionnaires) and should be discarded: MBTI (PerfectMatch), DISC (ThomasKnowsPeople), Enneagram (Dopasowani) or other proprietary ipsative tests like the ones used at Chemistry, ButterfliesAgain, Doskonalapara, PembePanjur, LittleHint, oneGoodLove and others.
NORMATIVE personality tests like Big5 versions used at PlentyOfFish, eHarmony, Meetic Affinity, Parship, Be2, True are good for orientative purposes but not good enough for predictive purposes.
http://onlinedatingsoundbarrier.blogspot.com/2011/11/big-summary-about-matching-algorithms.html
WorldWide, there are over 5000 -five thousand- online dating sites... but no one is using the 16PF5 to assess personality of their members!
Sunday, January 29, 2012
Who's Telling You The Truth About Dating Algorithms?
The online dating industry is a USD4 billion business (global market). [USD 4,000 million]
"... Dr. Eli Finkel (Northwestern University), Schwartz's younger colleague in the behavioral sciences, who staked out his own territory as industry-scold, denouncing eHarmony, one of the largest dating sites in the world and the first to market a scientific approach to matching. eHarmony has refused to reveal its algorithm, Finkel said, and therefore the company should not advertise a scientific approach to matching until it can show, publicly, that its system works according to the standards of scientific rigor. "
"... Dr. Eli Finkel (Northwestern University), Schwartz's younger colleague in the behavioral sciences, who staked out his own territory as industry-scold, denouncing eHarmony, one of the largest dating sites in the world and the first to market a scientific approach to matching. eHarmony has refused to reveal its algorithm, Finkel said, and therefore the company should not advertise a scientific approach to matching until it can show, publicly, that its system works according to the standards of scientific rigor. "
Sunday, January 22, 2012
One year ago, during Miami iDate2011 conference
Friday, January 20, 2012
Monday, January 16, 2012
Comiingle
A new social dating site, Comiingle, will be a stupid investors series' case of study.
Experience had shown serious daters do not tolerate friends / parents / neighbours / relatives / fans or other social networking users to be involved in a private matter as building a personal relationship with future in mind because they are "interested third parties ingredients" in a process that only concerns 2 persons. See failed proposals like SmartDate, HowAboutWe, Zoosk, Zin.gl, Engage (then rebranded to Ignighter group dating), Thread, Triangulate, Gelato (then rebranded to Twnty), WooMe, 12Like, LittleHint.
Remember:
Social networking/applications could merge with online dating for fun, for flirting, for entertainment purposes, for instant gratification.
Social networking and online dating for serious daters are like water and oil, they will never mix.
Online Dating for serious daters does not need to be more social, it needs to be more effective/efficient. It needs to reduce the false positives problem.
The Online Dating Industry needs innovations but they will come from only one source: the latest discoveries in theories of romantic relationships development with commitment.
Compatibility is all about a high level on personality* similarity* between prospective mates for long term mating with commitment.
*personality measured with a normative test.
*similarity: there are different ways to calculate similarity, it depends on how mathematically is defined.
Experience had shown serious daters do not tolerate friends / parents / neighbours / relatives / fans or other social networking users to be involved in a private matter as building a personal relationship with future in mind because they are "interested third parties ingredients" in a process that only concerns 2 persons. See failed proposals like SmartDate, HowAboutWe, Zoosk, Zin.gl, Engage (then rebranded to Ignighter group dating), Thread, Triangulate, Gelato (then rebranded to Twnty), WooMe, 12Like, LittleHint.
Remember:
Social networking/applications could merge with online dating for fun, for flirting, for entertainment purposes, for instant gratification.
Social networking and online dating for serious daters are like water and oil, they will never mix.
Online Dating for serious daters does not need to be more social, it needs to be more effective/efficient. It needs to reduce the false positives problem.
The Online Dating Industry needs innovations but they will come from only one source: the latest discoveries in theories of romantic relationships development with commitment.
Compatibility is all about a high level on personality* similarity* between prospective mates for long term mating with commitment.
*personality measured with a normative test.
*similarity: there are different ways to calculate similarity, it depends on how mathematically is defined.
Sunday, January 8, 2012
the Obsolescence of Dating Sites
Have you noticed the Obsolescence of Dating Sites offering Compatibility Matching Methods ?
eHarmony, Chemistry, True, PerfectMatch, Parship, MeeticAffinity, MatchAffinity, FriendScout24 BQ check, PlentyOfFish (POF) Chemistry Predictor, Be2; all of them are all RUBBISH for serious daters!
I am anxiously waiting the new sites to be launched by eHarmony Inc. and IAC's Personals!
Friday, January 6, 2012
The 5 steps in eHarmony Japan's questionnaire.
eHarmony Japan (ready since September 2011?) NEVER LAUNCHED.
Its questionnaire includes 5 steps.
Step #1 Basic information. (8% of the whole questionnaire)
Step #2 Self-introduction including personality traits assessment. (45% of the whole questionnaire)
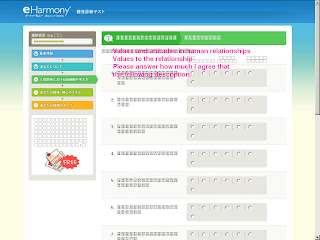
Step #3 Values and Attitudes in Human Relationships. (21% of the whole questionnaire)
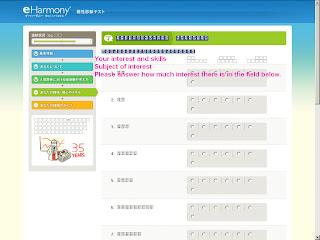
Step #4 Interests and Skills. (20% of the whole questionnaire)
Step #5 Your Ideal Match. (6% of the whole questionnaire)
Thursday, January 5, 2012
The eHarmony Japan mystery
It seems eHarmony Japan was live, ready, fully developed since September 2011 but never launched.
Why?
Its subscribe offer says "3 months free from 6 October 2011 to 31 December 2011"?
Wednesday, January 4, 2012
eHarmony's matching algorithm, the truth. part 1 of 3
eHarmony has 2 bogus patents about its Compatibility Matching Algorithm, none of them explains in detail the actual Compatibility Matching Algorithm in use in their sites.
eHarmony, a 11+ years old obsolete site, uses a Compatibility Matching Algorithm based on personality similarity with the Big5 normative personality test and Dyadic Adjustment Scale (invented by Dr. Graham B. Spanier in 1976) as its core. The Guided Communication Process (a mutual filtering step) is an appendix of its main matching algorithm.
eHarmony is not "scientifically proven" because eHarmony Labs could not prove eHarmony's matching algorithm can match prospective partners who will have more stable and satisfying relationships -and very low divorce rates- than couples matched by chance, astrological destiny, personal preferences, searching on one's own, or other technique as the control group in a peer reviewed Scientific Paper.
eHarmony's Compatibility Matching Algorithm consists of 2 stages.
* A mutual filtering stage common to any online dating site like PlentyOfFish, Match, Chemistry, True, PerfectMatch, Parship, MeeticAffinity, OkCupid, Be2, FriendScout24, etc.
* The core stage.
The mutual filtering stage includes your race, age range, physical appearance, income, religion, leisure activities and sports, skills, location, drinking and smoking habits, likes & dislikes, if you want children or if you have children under 18 living with you, pets, etc. and the same items you will desire in any prospective partner.
The core stage of eHarmony's Compatibility Matching Algorithm:
1) The normative Big5 test to assess personality (The Big 5 is good for orientative purposes but not good enough for predictive purposes)
2) Dyadic Adjustment Scale (invented in 1976) to calculate compatibility (similarity) between prospective mates.
3) The Guided Communication Process (a mutual filtering step) designed to narrow even more the field of persons you give a better chance of getting along with, and also it is useful for feedback purposes.
(to be continued in part 2)
eHarmony claims 12 million users and Match Latam, 30 million
In 2012 eHarmony claims 12 million users.
In Latin America, Match claims 30 million users.
But how many of those 12 million users claimed by eHarmony are active?
My bet: less than 1 million, so 1M/12M is 8.33%.
8.33% of eHarmony's database is useful.
The rest, 11 million are inactive or fake profiles!!!
As for Match Latam, which also owns Meetic (ParPerfeito in Brazil), my bet is: only 200,000 paying members in Latin American countries (Brazil, Mexico, Colombia, Venezuela, Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Uruguay, Paraguay, Ecuador)
200,000/30M is 0.67%, i.e. less than 1% of Match Latam database is useful.
Tuesday, January 3, 2012
SPSP 2012 series of posters
The Thirteenth Annual Meeting of the Society for Personality and Social Psychology
will be held January 26-28, 2012, in San Diego, California.
will be held January 26-28, 2012, in San Diego, California.
Gian Gonzaga1, Heather Setrakian1, Erina Lee1; 1eHarmony Labs
Poster B322, Friday, January 27, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
This study investigated how personality similarity related to relationship satisfaction among committed gay and lesbian couples. Couples who were more similar in personality reported higher levels of relationship satisfaction after controlling for stereotype similarity and the main effects of personality. Implications for understanding the underpinnings of relationship commitment are discussed.
Bigger May Be Better: Female Attraction to Male Muscle Mass Across the Menstrual Cycle
Ashalee C. Hurst1, Robert D. Mather2; 1Texas Tech University, 2University of Central Oklahoma
Poster A81, Thursday, January 26, 7:00 – 8:30 pm, Sails Pavilion
Female attraction to male muscle was investigated throughout the menstrual cycle. Participants rated male bodies with low, medium, high, and extremely high muscle. No significant interaction between ovulation and muscle appeared. A significant main effect for muscle appeared. Extreme, high, and medium muscle were each rated higher than low muscle.
“Psssst, is My Personality Showing?” Exploring Facebook and Personality
Britni Brewer1; 1High Point University
Poster D71, Friday, January 27, 6:15 – 7:45 pm, Sails Pavilion
Social relationships are becoming increasingly popular in online environments but little research has been conducted on individual differences in utilization of social media. This study examines the relationship between personality and Facebook behaviors. The results indicate self-reported behavior may not present the same relationships as seen with more objective measures.
Personality Predicts Research Preferences: Big Five Predicts How Individuals Perform Information Searches
Kimdy Le1, Olivia Pavlov1, Joan Poulsen1, Emily Dill1; 1Indiana University Purdue University - Columbus
Poster D116, Friday, January 27, 6:15 – 7:45 pm, Sails Pavilion
This study tested how personality relates to information-source preference. We presented participants with 10 scenarios. Participants rated the likelihood of using 5 sources of information for each scenario. We found that personality was related to information-source preference, and we tested for mediation and moderation. In sum, personality predicted information-source preferences.
The Enemy Effect: Perceptions of Similarity as a Function of Attraction
Brian Collisson1, John Chambers1; 1University of Florida
Poster E142, Saturday, January 28, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
Similarity breeds attraction (Byrne, 1971), but does attraction also breed perceived similarity? The current research addresses this question by examining the inferences people make towards a likable and dislikable other. Findings suggest that perceiving similarity as a function of attraction establishes cognitive balance and consistency within the individual (Heider, 1958).
Birth Cohort Differences in the Big Five Personality Traits, 1985-2009: A Cross-Temporal Meta-Analysis
Brittany Gentile1, W. Keith Campbell1, Jean M. Twenge2; 1University of Georgia, 2San Diego State University
Poster D119, Friday, January 27, 6:15 – 7:45 pm, Sails Pavilion
Multiple meta-analyses were conducted to examine generational change over time in Big Five personality traits among college students using four well-known measures (i.e., Big Five Inventory, NEO-FFI, NEO-PI, and NEO-PI-R). Results show a significant decrease in openness across several measures. Partial evidence was found for changes in neuroticism and extraversion.
Narcissism and First Impressions in a Speed-Dating Study
Robert Ackerman1; 1Michigan State University
Poster E148, Saturday, January 28, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
A speed-dating paradigm was used to clarify the roles played by different narcissistic traits in the generation of romantic appeal. Undergraduate students (n = 232) completed the Narcissistic Personality Inventory and engaged in five-minute speed dates. Results highlighted the importance of grandiosity in the first impressions of narcissists.
The effects of race and trait information on ratings of dating desirability: A behavioral and event-related potential investigation.
Holly Earls1, Mark Varvaris1, James Morris1; 1University of Virginia
Poster A42, Thursday, January 26, 7:00 – 8:30 pm, Sails Pavilion
This study utilized behavioral and event-related potential measures to assess the role of race, trait information, and attraction in the formation of romantic relationships across genders. Converging evidence from both experiments indicate that race and trait information have a larger impact on dating desirability for females than for males.
Dispositional Factors Predicting Usage of and Behavior on Online Dating Sites
Jennifer Fitzpatrick1, Ginette C. Blackhart2; 1East Tennessee State University
Poster D198, Friday, January 27, 6:15 – 7:45 pm, Sails Pavilion
This study assessed the relationship between several dispositional variables and online dating site usage and behavior. Results showed self-esteem, sexual preference, rejection sensitivity, and age to be significant predictors of usage of online dating sites. Self-esteem, gender, and age were significant predictors of behavior related to online dating.
Emotional responses to an acute elicitation of jealousy in dating couples
Nicole E. Henniger1, Christine R. Harris1; 1University of California, San Diego
Poster B148, Friday, January 27, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
We ethically induced jealousy in dating couples by making it appear as if one partner was flirting with another participant in an online chat. Participants who viewed a flirtatious versus mundane conversation reported significantly more jealousy and other negative emotions. Attachment style was not related to differences in responses.
Relationship Outcomes in Married and Dating Couples: Attributions, Satisfaction, and Closeness
Brooke M. Montoya1, Alicia Limke2, Paul C. Jones1; 1Southern Nazarene University, 2University of Central Oklahoma
Poster E57, Saturday, January 28, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
105 participants completed measures of relationship outcomes. Married individuals reported higher levels of strength (a form of closeness) than did dating individuals; however, there were no differences between dating and married individuals in internality, stability, or globality of negative attributions, relationship satisfaction, or the diversity or frequency of couples’ activities.
How Do I See You? Partner-Enhancement in Dating Couples
Marian Morry1, Mie Kito2; 1University of Manitoba, 2University of Winnipeg
Poster C58, Friday, January 27, 12:30 – 2:00 pm, Sails Pavilion
Individuals self-enhance relative to strangers or acquaintances. According to self-expansion theory, dating partners become associated with the self. Therefore, people can perceive the self positively by viewing their partner positively. Repeated-measures ANOVAs indicated partner-enhancement and idealization on moderate but not low relationship relevant traits among 58 heterosexual dating couples.
Backfire effect: Emphasizing reproductively advantageous male traits in a dating prime engenders lower female interpersonal attraction
Chia Niap Tan1, Fen-Fang Tsai2; 1National University of Singapore, 2Department of Psychology, National University of Singapore
Poster E158, Saturday, January 28, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
Addressing the inadequacies of the Evolutionary axiom of interpersonal attraction, this study depicts how indiscriminate emphasis of reproductively advantageous male traits can backfire even in a dating prime. By considering several other premises, a working model for attraction can be generated that is both coherent with theory and yet generalizable.
Attachment and the Use of Humor during Conflict Negotiation in Dating Couples
Heike A. Winterheld1, Jeffry A. Simpson2, M. Minda Oriña3; 1California State University, East Bay, 2University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Campus, 3St. Olaf College
Poster C72, Friday, January 27, 12:30 – 2:00 pm, Sails Pavilion
We tested how partners with different attachment orientations express and react to humor during conflict negotiation. Avoidant individuals used less affiliative and more aggressive humor; anxious individuals used more self-defeating humor. Avoidant individuals were angrier when partners used aggressive humor. Anxious individuals responded favorably to affiliative but not self-defeating humor.
“Be Mine”: Individual differences in attachment orientation predict relationship investment on Valentine’s Day
William J. Chopik1, Britney M. Wardecker1, Robin S. Edelstein1; 1University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Poster E38, Saturday, January 28, 8:00 – 9:30 am, Sails Pavilion
In two studies we examined how Valentine’s Day affects perceptions of investment in romantic relationships. We found that adult attachment orientation moderated how people evaluated their relationships on Valentine’s Day compared to a control day. Findings are discussed in the context of the relationship-enhancing events, such as holidays and anniversaries.
Sunday, January 1, 2012
eHarmony is going social
eHarmony is going social with Facebook connect and the Ping a Friend feature. See screenshots as proof.
"With Ping a Friend, you can get advice about a match's profile from up to 5 friends anywhere in the world, via Facebook. Uncertain about a match? Ping a Friend!"
Yes, you read well, eHarmony's Team to cannibalize eHarmony (a 11+ years old obsolete site) making it a social dating site meanwhile they are developing a completely new site, a new compatibility matching algorithm using the 16PF5 test, instead of the Big5.
Many old dating sites like Match and PlentyOfFish (POF) had made the same trick, they show themselves as social dating sites.
Remember: Social networking/applications could merge with online dating for fun, for flirting, for entertainment purposes, for instant gratification. Social networking and online dating for serious daters are like water and oil, they will never mix.
Online Dating for serious daters does not need to be more social, it needs to be more effective/efficient. It needs to reduce the false positives problem.
The Online Dating Industry needs innovations but they will come from only one source: the latest discoveries in theories of romantic relationships development with commitment.
Only 3 major discoveries can help to revolutionize the online dating industry.
I) Several studies showing contraceptive pills users make different mate choices, on average, compared to non-users. "Only short-term but not long-term partner preferences tend to vary with the menstrual cycle"
II) People often report partner preferences that are not compatible with their choices in real life. (FORGET Behavioural recommender systems or other system that learns your preferences)
III) What is important in attracting people to one another may not be important in making couples happy. Compatibility is all about a high level on personality similarity between prospective mates for long term mating with commitment.
OkCupid Labs, part of Match's Team, is developing a very advanced compatibility matching method using the normative personality test 16PF5 to be launched in an independent site to replace Chemistry.
eHarmony Labs, the same, developing a very advanced compatibility matching method using the normative personality test 16PF5 to be launched in an independent site.
I had challenged both eHarmony and Match to show those Compatibility Distribution Curves for each and every dater, i.e. how compatible you are with the rest of the daters.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)